Manhole Rehabilitation
Manholes are critical access points for the assessment, maintenance, and repair work of the entire underground infrastructure system. Thus, they must be properly maintained and kept in good condition to carry out quick repairs, and – most importantly – to prevent injury to workers who use these manholes for access to the system. There are many trenchless technologies for the rehabilitation of manholes, including specialty products installed to primarily stop leakage, as well many options for structural enhancement and corrosion protection.
Applications
Cementitious Coating Systems
These materials are either spray (low pressure) or trowel applied. They have a long, established history with recent improvements in fast setting high strength corrosion resistant mortars. Some are reinforced with fibers for added tensile strength and crack resistance.
Chimney Seals
Specialty products such as mechanical seals, hand applied coatings, external wrap materials, etc. are designed to address specific infiltration and/or inflow concerns such as leaks between the manhole casting and the chimney and usually can be applied with a minimum of labor and equipment.
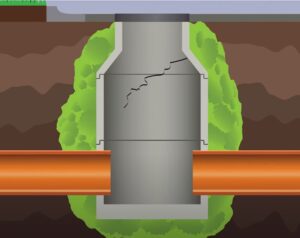
Cured-In-Place Manhole (CIPM) Liner
These systems utilize a variety of resins. They are used for renewal of the manhole structure, have excellent chemical resistance and strong, long-term physical properties. Typical methods and equipment for installation can line diameters from 2 ft to 10 ft and up to 60 ft deep. Liners are typically designed for full depth hydrostatic head conditions and to withstand earth pressure and traffic loading. They can also be designed as a stand-alone structure.
Cured-In-Place Manhole Tube Liner
The CIPMH (cured-in-place manhole) liner is a unique one-piece liner made to fit all manholes including barrel sections, eccentric and concentric cones constructed of brick and mortar, pre-cast or block. CIPMH for chimney or full-depth manhole repair eliminates infiltration & inflow through manhole walls. The universal sized manhole liner is engineered to resist freeze-thaw cycles and create a watertight, corrosion resistant lining.
Polymer Coating Systems
Epoxy
Solvent free (100% solids) coatings are operator and environmentally safe and require no evaporative curing process making them ideal for underground coating applications. These high build coatings are either spray or trowel applied and can be specified at structurally enhancing thicknesses. Current generations of epoxy coatings will adhere to moist or damp substrates and have excellent chemical resistance and long-term physical properties.
Urethane
These materials are typically spray applied. Many variations are available from elastomeric to rigid formulations. Generally, they are 100% solids only used for underground coating, but can be adapted to use in environments where UV exposure exist. They have good to excellent chemical resistance and elastomeric qualities that range from rigid formulations to highly flexible. Urethanes generally have strong long-term physical properties. A hallmark of the urethane family is their quick-curing capacity which allows for a rapid “return to service” for the structures that are coated.
Fiberglass Inserts
Generally, the top of the old manhole is cut off and removed and the interior is pressure washed to remove any debris and loose material. The channel is typically removed and replaced after the installation of the pre-cast inserts. If this is not possible, the precast manhole inserts can be shaped to fit the existing bench configuration. The precast inserts typically come in either one continuous section or in different lengths for easy assembly.
Geopolymer Coatings
Geopolymer cements can be used to restore a manhole’s structural integrity and permanently stop infiltration and corrosion. A variety of structural and corrosion resistant products are on the market.

Manhole Grouting
Manholes are a significant contributor to inflow and infiltration into the collection system. Groundwater enters through vertical cracks, horizontal joints, and pipe penetrations in precast systems, and through numerous parts of brick-and-mortar manholes. One application called curtain grouting –completely encapsulates the structure with acrylamide grout. Curtain grouting is executed from within the manhole (confined space entry required) and allows you stop multiple leaks at the same time. The process begins by drilling a series of holes in a grid pattern through the manhole walls. Grout is then injected through the drill holes into the surrounding soil, encapsulating the structure, and creating an impermeable waterproof barrier. Other methods of sealing manholes with urethane grouts take advantage of highly expansive materials that can seal cracks and fill large voids outside the structure.
Chimney/Frame Seals, Liners and Joint Seals
Used to seal the casting/chimney and wall area against leakage into the manhole. Capable of withstanding surface traffic impact and freeze/thaw pressures.
Panel Liners
Plastic panel that is glued to the manhole wall with a pre-applied mastic on the structure. Generally unaffected by water vapor pressure, characteristics include resistance to corrosive environments, monolithic protective coating, encapsulation all areas of the manhole structure, is pin-hole free, stops infiltration and is bonded to the host structure.
Removable Forms
Poured-in place concrete manhole reconstruction includes the formation of a new integrated liner wall within the existing manhole structure. The new manhole liner wall generally conforms to the existing inside dimension and is often combined with epoxy coating, or a plastic (HDPE or PVC) liner for corrosion protection.
Thermoplastic Sheet Lining Systems
These systems have an extensive installation history. Excellent chemical resistance with both PVC and HDPE sheet materials; they are typically used with cementitious or polymer mastic basecoats.